Each year at ARVO, dozens of papers and posters are presented on futuristic refractive procedures and prospective IOL materials. While such cutting-edge information is of great interest, maintaining a healthy and quiet ocular surface continues to be optometry’s primary role in the refractive care process.
So, in addition to previewing some of the latest surgical procedures and enhanced diagnostic equipment, we’ll examine an abundance of research surrounding several new topical agents that will help maximize patients’ postoperative outcomes.
Advances in Epidemiology
Although we are all experienced in acute disease management, it is often helpful to understand both how and why some patients are more likely than others to develop certain ocular conditions. Such information can add valuable guidelines to public health initiatives––particularly with regard to conditions that are precipitated by modifiable lifestyle factors.
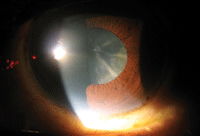
Excessive consumption of foods rich in refined sugars, such as white rice, increases an individual’s risk of cataracts. Photo: Marc D. Myers, OD, and Andrew S. Gurwood, OD
For example, we now have a better understanding of how dietary intake can influence the rate of cataract development and progression. An Indian study of 3,723 patients uncovered a significant association between frequent consumption of high-glycemic index foods (e.g., white rice, potatoes, pasta) and cataract development.895/B0119 To reduce the incidence of cataracts, the researchers recommended consumption of several low-glycemic index cereals in lieu of foods rich in refined sugars.
Additionally, obesity may affect corneal pachymetry measurements during a refractive consultation. A study from the United Kingdom indicated that peripheral corneal thickness was inversely proportional to body mass index (BMI).524/B0161 While the study was confined to healthy males with average BMIs, the researchers suggested that body mass index should be added as an input line parameter on corneal analyzers.
Dialed-up Diagnostic Tech
We now may be able to document more accurate and repeatable measurements in patients with abnormal corneas. A new color LED corneal topographer (Cassini, i-Optics) was validated against conventional Placido disk- and Scheimpflug-based topographers in eyes that underwent penetrating keratoplasty.528/B0165 The device was shown to be more accurate than Placido disk topographers at measuring non-symmetric aberrations, such as astigmatism and quadrafoil. Further, measurements from the color LED topographer were more repeatable than those derived by Scheimpflug-based units. This technology may prove to be especially valuable in refractive surgery clinics that receive a high volume of patients with abnormal corneas.
A Boston-based research group used in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) to demonstrate a profound increase in immune dendritic cells and significant decrease in corneal nerves in patients with post-LASIK keratoneuralgia.3711/371 Despite minimal findings on clinical exam, subclinical changes in sub-basal nerves––as well as increased immune and inflammatory cells––were seen on IVCM.
It’s important to note that the IVCM findings correlated well with symptoms. The researchers concluded that IVCM might yield new insights into the pathogenesis of otherwise unexplained corneal pain.
A Focus on Contrast Sensitivity
In a Department of Defense-funded joint study between the Wilmer Eye Institute and several military centers, two conventional LASIK technologies were evaluated for postoperative visual performance via contrast sensitivity assessment.3125/D0060 In this study, wavefront-guided (WFG) surgeries were performed using the VISX Star S4 (Abbott Medical Optics) and wavefront-optimized (WFO) were conducted with the Wavelight Allegretto Wave Eye-Q (Alcon). Corneal flaps were created using the IntraLase (Abbott Medical Optics) femtosecond laser system.
The researchers evaluated best-corrected visual acuity and small-letter (20/25) contrast sensitivity, as well as low luminance/night vision through a night-vision filter. They concluded that high-contrast visual acuity was comparable between WFO and WFG LASIK––as would be anticipated. Perhaps more importantly, however, they found that WFG LASIK appears to be superior to WFO LASIK regarding postoperative night vision performance and low-contrast acuity.

The PhysIOL FineVision trifocal IOL demonstrated good contrast sensitivity scores. (Note: This lens is not commercially available in the US.) Photo: PhysIOL
Additionally, visual outcome and patient satisfaction data was presented on a new diffractive trifocal intraocular lens.841/B0065 The FineVision trifocal IOL (PhysIOL) was evaluated in 50 eyes of 25 patients. The results showed that photopic contrast sensitivity was within the standard normal range. The rate of spectacle independence for all the distances was higher than 85%, and a low percentage of patients reported significant halo or ghosting.
New Developments in CXL
Although corneal collagen crosslinking (CXL) with riboflavin is not approved in the United States, the procedure continues to be routinely performed and extensively studied throughout the world. CXL is highly effective at arresting keratoconus progression secondary to enhanced corneal rigidity. However, when being applied to the corneal tissue, the procedure is fundamentally non-specific.
Some advanced research involving topography guidance was presented that could help transform CXL into a legitimate refractive procedure.529/B0166 With a stabilizing eye tracker and overlaid topographical data, a digital micromirror could be used to control the applied UVA pattern. Soon, practitioners not only may be able to halt keratoconus, but also provide the patient with freedom from glasses or contact lenses.
In a similar study, researchers from the Cleveland Clinic evaluated the possibility of selective CXL to alter corneal astigmatism.1620/D0255 In their assessment model, treatments applied orthogonal to the steep axis decreased astigmatism. This could serve as a novel, noninvasive method of astigmatism correction––not only in diseased corneas, but also in healthy eyes.
Improved Patient Safety
Lens exfoliation syndrome (LES) poses significant intraoperative risks during cataract surgery due to weak lens zonules. Femtosecond laser-assisted clear cornea cataract surgery in LES appeared to be safe and effective in a multi-country study involving 65 eyes of 48 consecutive patients.1818/A0164
Corneal collagen crosslinking, as seen here, may be combined with a topography guidance system to surgically correct refractive error.
The study analyzed uncorrected visual acuity, best spectacle-corrected visual acuity, refraction, cylinder, capsulorhexis diameter, topographic cylinder change and endothelial cell count, as well as possible complications. The researchers suggested that femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery might hold an intrinsic advantage of less zonular weakening associated with capsulorhexis and lens fragmentation.
Pre- and Postoperative Dry Eye Treatment
Advanced laser systems, cutting-edge diagnostic technology and enhanced lens materials have dramatically improved the precision and safety of refractive surgical procedures during the last decade. Even so, our patients still regularly experience postoperative dryness and ocular surface inflammation. Fortunately, a handful of novel topical agents may help reduce these deleterious side effects and facilitate optimized visual outcomes.
A multi-university animal study showed that topical omega-3 fatty acid eye drops can improve corneal irregularity, reduce epithelial barrier disruption, and decrease inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers on the ocular surface.901/B0206
Following topical administration of 0.2% omega-3 drops, 0.1% hyaluronic acid drops or mixture of both agents, corneal irregularity and fluorescein staining scores were measured at both five- and 10-day follow-up. Levels of interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-17 and interferon gamma-induced protein (IP)-10 were measured in the conjunctiva using a multiplexed immunobead-based assay at 10 days.
Mice treated with the combination 0.2% omega-3 and 0.1% hyaluronic acid mixture showed a significant improvement in corneal irregularity and fluorescein staining compared to mice treated with just 0.1% hyaluronic acid. Further, mice that received the mixture exhibited a significant decrease in IL-1beta, IL-17 and IP-10 levels, compared to the other two dosing groups. These results suggested that a combined mixture of 0.2% omega-3 fatty acid and 0.1% hyaluronic acid can be useful for preoperative treatment of dry eye and corneal irregularity.
A Finnish study analyzed the potential use of topical cis-urocanic acid (cis-UCA) in a murine model of dry eye in mice.902/B0207 Compared to the both the vehicle and Restasis (cyclosporine, Allergan) treatment groups, the researchers found that 1.0% cis-UCA was most effective in reducing corneal fluorescein staining. Interestingly, mice treated with Restasis showed no statistical separation throughout the experiment, and did not exhibit a significant reduction in corneal staining at day 17 of treatment. They concluded that topical treatment with 1.0% cis-UCA significantly reduced corneal staining in a pre-clinical model of dry eye disease.
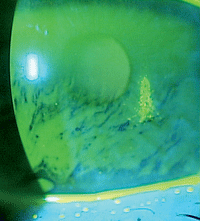
A topical mixture of 0.2% omega-3 and 0.1% hyaluronic acid could be used to decrease epithelial barrier disruption and corneal staining in dry eye patients. Photo: Mile Brujic, OD
A murine study conducted at the Brien Holden Vision Institute indicated that topical application of L-carnitine could limit the progression and severity dry eye.921/B0226 Eye drops containing L-carnitine have been shown to produce rapid and consistent improvements in the signs and symptoms of dry eye disease. The researchers reported that L-carnitine could help maintain human corneal epithelial cell volume under hyperosmotic stress, as well as ameliorate aspects of hyperosmotic stress-induced apoptosis.
A Japanese study evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of rebamipide in human corneal epithelial cells.911/B0216 Dry eye causes tear hyperosmolality, which stimulates an inflammatory cascade and disrupts corneal barrier function. Rebamipide––which exhibits mucin secretagogue activity––is used regularly as a dry eye treatment in Japan.
The researchers documented the effects of rebamipide on barrier function and cytokine expression in a human corneal epithelial cell line. They found that, in conjunction with its mucin secretagogue activity, rebamipide effectively treats dry eye via up-regulation of barrier function and anti-inflammatory effects.
In a separate study, researchers analyzed the clinical effect of rebamipide on post-LASIK dry eye.945/B0250 This prospective study evaluated 32 eyes of 16 patients with LASIK-associated dry eye who currently used artificial tears or hyaluronic acid eye drops. In addition to their current topical therapy, the subjects received 2.0% rebamipide eye drops QID for four weeks.
Tear secretion was examined via Schirmer testing with anesthesia both before rebamipide treatment and at four-week follow-up. Additionally, the researchers measured tear film break-up time, fluorescein staining and lissamine green staining before treatment and at both one- and four-week follow-up.
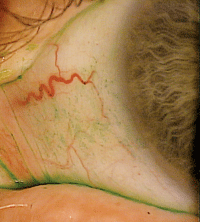
Phase III study data indicated that, compared to placebo, Lifitegrast 5.0% (SARcode Biosciences) dramatically reduced the signs of conjunctival lissamine staining. Photo: Mile Brujic, OD
The researchers determined that the addition of 2.0% rebamipide improved ocular surface function and dry eye symptoms. More specifically, they noted that increased mucin secretion in the tear film effectively improved LASIK-associated dry eye following rebamipide use.
A recently completed Phase III FDA study was presented on a new agent for dry eye disease––Lifitegrast 5.0% ophthalmic solution (SARcode Biosciences).2669/309 This may be the closest-to-market dry eye formulation that we’ve seen in years, and could hold major promise for the management of both pre- and postoperative ocular surface disease.
Lifitegrast is an investigational drug that targets integrin lymphocyte antigen-1 (LFA-1) and inhibits binding to intracellular adhesion molecule-1. LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions are essential to the regulation of T-cell-mediated inflammation.
The study evaluated 588 dry eye patients over 84 days, measuring corneal staining and ocular symptoms. Compared to placebo, Lifitegrast ophthalmic solution demonstrated a superior ability to reduce corneal fluorescein and conjunctival lissamine staining––both key clinical parameters of ocular surface disease. Further, reductions in staining were associated with significant improvements in key symptoms. The researchers determined that Lifitegrast appears safe and well-tolerated when administered BID for at least 84 days.
Enhanced Postoperative Healing
Medical treatment following refractive surgery often involves the use of several medications. Many of the most commonly used drugs are preserved with benzalkonium chloride (BAK)––which is known to impair the integrity of tear film lipid layer and the corneal epithelial membranes.
One study showed that hyaluronic acid was able to efficiently suppress the adverse effects of BAK on the meibomian and corneal lipid films.944/B0249 The researchers were able to demonstrate this by instilling pure BAK into the lipid films. The interaction yielded impaired lipid film spreading, increased surface pressure-area hysteresis and partial lipid displacement from the ocular surface.
The inclusion of hyaluronic acid in the lipid film’s subphase minimized these adverse effects. Once a concentration ≥ 0.1% of hyaluronic acid was added, normal lipid film properties were maintained for the entire BAK concentration range. This could have immediate consequences for current patient care, and likely will lead to new formulations of eye drops intended for postoperative care.
Meanwhile, a French study evaluated the effects of hyperosmolar conditions and increased BAK toxicity on corneal wound healing efficacy.6041/A0104 Cytotoxicity, cell migration and proliferation were analyzed after a 30-minute exposure to 0.02% BAK in a normal osmolarity state (275mOsm/L), 0.02% BAK in three different hyperosmolar states (356mOsm/L, 406mOsm/L and 505mOsm/L) or phosphate-buffered saline. The researchers noted that BAK-induced hyperosmolarity and/or BAK toxicity impairs the corneal healing process and exacerbates dry eye conditions.
During the last several years, there has been industry-wide interest in the formulation of topical postoperative medications that exhibited reduced dosing intervals and limited side effect profiles. In a Phase III FDA trial, researchers evaluated the anti-inflammatory effects of a low-concentration formula of bromfenac in cataract surgery patients.125/C0130
Subjects underwent unilateral cataract surgery (phacoemulsification or extracapsular cataract extraction) with posterior chamber IOL implantation and were randomized to receive either the low-concentration bromfenac ophthalmic solution or placebo once daily.
Dosing began one day before cataract surgery and was continued postoperatively for 14 days. At day three, 27.9% of subjects in the bromfenac group achieved trace ocular inflammation vs. just 13.8% in the placebo group. By day 15, 71.2% of patients on bromfenac therapy exhibited trace inflammation vs. 39.4% of patients in the placebo group.
The researchers also determined that, when compared to placebo, QD low-concentration bromfenac ophthalmic solution yielded a lower overall incidence of ocular adverse events in postoperative cataract surgery patients. (Note: Since the initial submission of this study to ARVO, this specific formulation of bromfenac has been FDA approved as Prolensa [bromfenac ophthalmic solution 0.07%, Bausch + Lomb]).

