 |
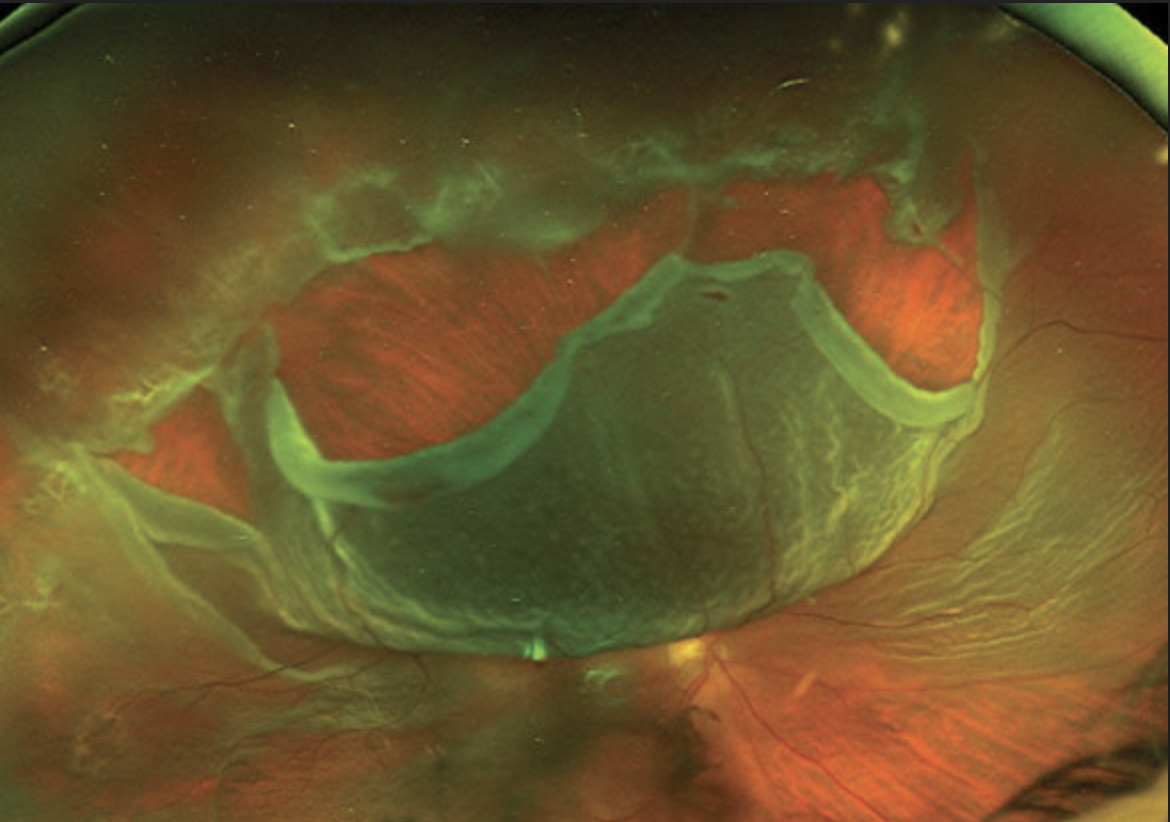
| RRD risk is associated with age, sex and season, among other factors. Photo: Mohammad Rafieetary, OD. |
In an effort to paint a clearer picture of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), retinal break and posterior vitreous detachment (PVD), researchers recently reported that, within the IRIS Registry, the highest incidence of RRD was in the sixth and seventh decade of life, the higher incidence of RRD repair and retinal break treatment in men combined with the higher incidence of PVD in women suggests an inherent sex-related risk and the seasonal variation associated with national holidays was less pronounced for RRD repair and retinal break treatment.
This retrospective database study included patients in the IRIS Registry who underwent RRD repair, retinal break treatment or cataract surgery. Daily incidence rates were defined as the ratio of the number of patients who underwent RRD repair or retinal break treatment and the number of patients diagnosed with PVD to the number of patients followed on a given day within the IRIS Registry. The cataract surgery group was included as a means of comparison for seasonal variation given its elective nature. Rates were stratified by decade of life, sex and race.
Of the 7,115,774 patients who were diagnosed with incident PVD during the study period, 237,646 underwent RRD repair and 359,022 had retinal break treatment. A total of 5,940,448 cataract surgery patients were also included.
The mean daily incidences within the IRIS Registry for RRD repair, retinal break treatment, PVD diagnosis and cataract surgery were 0.46, 0.70, 13.90 and 11.80 per 100,000 patients, respectively. Men had a higher incidence of RRD repair and retinal break treatment, whereas women had a higher incidence of PVD diagnosis. RRD incidence was higher in Caucasians. Seasonal decreases in PVD, retinal break treatment, RRD repair and cataract surgery corresponded to national holidays with larger decreases in winter months. Kaplan-Meier estimates showed that RRD repair and retinal break treatment typically occurred within 60 days of PVD diagnosis.
“We believe our findings contribute valuable insights to the epidemiology of RRD, retinal break formation and PVD on a scale that has not previously been examined,” the study authors concluded in their paper. “Future directions of study should be aimed both to understand the implications of the differences observed between demographic groups and expand datasets such as the IRIS Registry to collect more granular information that could help improve future investigations.”
Saraf SS, Lacy M, Hunt MS, et al. Demographics and seasonality of retinal detachment, retinal breaks and posterior vitreous detachment from the IRIS Registry (Intelligent Research in Sight). Ophthalmol Sci. March 18, 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. |


