 |
|
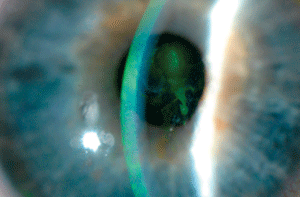
MMP concentration may dictate effective treatment strategies in corneal erosion patients. Photo: Aaron Bronner, OD. Click image to enlarge. |
Researchers believe that certain matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) may be to blame for defective corneal re-epithelization in patients with recurrent corneal erosions. MMPs degrade the junctional complexes that epithelial cells rely on in order to adhere to the basement membrane. In the study, MMP-2 and MMP-3 were found to dissolve the basement membrane and accumulate in the epithelium, possibly inducing erosion recurrence.
The study included 121 eyes. Patients were divided into two groups: a control group of 65 healthy patients with stable epithelial-stromal interface who qualified for epi-Bowman keratectomy (EBK) and a study group of phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) patients with recurrent corneal erosions and either Cogan’s microcystic dystrophy (n=22) or posttraumatic corneal erosions (n=34).
The researchers analyzed the corneal epithelium collected during PTK and EBK and determined MMP concentrations using an immunohistochemical assay. They found statistically significantly higher concentrations of MMP-2 and MMP-3 in the study group compared with the control group. The differences in concentrations of MMP-2 and MMP-3 in the recurrent corneal erosion subgroups weren’t statistically significant.
“Knowledge of MMP concentrations in the corneal epithelium of recurrent corneal erosion patients might substantially contribute to the optimization of treatment strategies,” the researchers wrote in their paper. They weren’t able to obtain other MMP concentrations in the corneal epithelium sufficient for analysis, but they noted that MMP-1 and MMP-9 concentrations in particular should be assessed in future studies since they have substrate specificity and increased activity in the acute phase of corneal erosion. Additionally, they pointed out that MMP-7 and MMP-8 warrant attention for their ability to degrade elements of the epithelial-stromal interface.
Jadczyk-Sorek K, Garczorz W, Bubała-Stachowicz B, et al. Increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-3 concentrations in corneal epithelium of patients with recurrent corneal erosions. Hindawi J Ophthalmol. September 25, 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. |

