 |
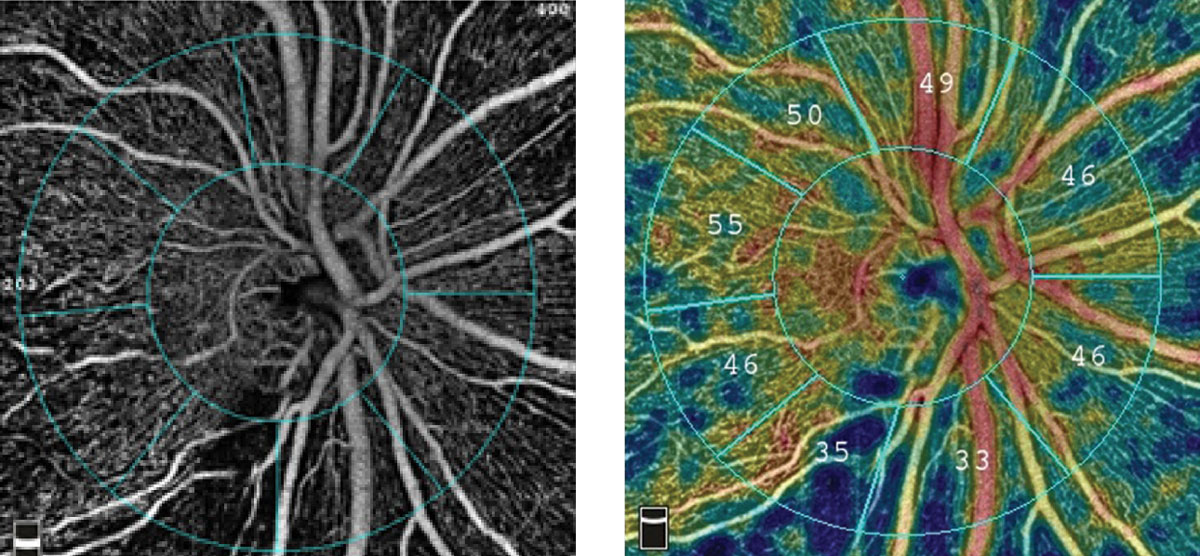
Macular vascular parameters correlate with RNFL thickness in early POAG cases. Photo: Optovue. Click image to enlarge. |
It has been suggested that as glaucoma progresses, the benefit of OCT parameters decreases due to the baseline effect, whereas the decrease in vascular density can be followed with OCT-A. While superior RNFL still has an important place in the diagnosis and follow-up of preperimetric glaucoma patients, researchers in Turkey propose that nasal circumpapillary vascular density, average circumpapillary vascular density and whole-image vessel density can be used as an adjunctive diagnostic tool in patients with suspected glaucoma.
Their study included a total of 27 patients with preperimetric glaucoma in one eye and early POAG in the fellow eye, as well as a control group consisting of 27 eyes of 27 healthy volunteers. All participants underwent OCT-A imaging. RNFL and macular ganglion cell complex (GCC) measurements were obtained simultaneously with vascular parameters. They also examined cpVD in eight sectors.
In preperimetric eyes, average RNFL thickness and whole-image vessel density had comparable diagnostic performance. Compared with the control group, preperimetric glaucoma eyes had significantly lower RNFL thickness in all quadrants except for the temporal quadrant, while circumpapillary vessel density differed only in the nasal inferior and nasal superior sectors.
“The finding of lower vessel density in these eyes suggests that OCT-A can detect microvascular changes in eyes at high risk of developing glaucoma, before there are detectable VF defects,” the study authors noted.
In early glaucoma eyes, circumpapillary vessel density differed significantly from controls in all sectors except for the inferotemporal, temporal inferior and temporal superior sectors, while perifoveal macular vascular parameters differed in all quadrants. This measurement was strongly correlated with RNFL thickness in the superior, nasal, and temporal quadrants and moderately correlated in the inferior quadrant.
“While OCT-A facilitates glaucoma follow-up through circumpapillary perfusion monitoring in preperimetric patients, it can also be considered an important modality for detecting changes in macular perfusion in early glaucoma,” the researchers concluded.
Turker O, Solmaz N, Onder F. Peripapillary and macular vascular density in patients with preperimetric and early primary open-angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma. June 21, 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. |


