 |
| Archway is the first successful Phase III trial of a continuous delivery system for a biologic agent into the vitreous. Photo: Anat Loewenstein, MD. Click image to enlarge. |
Investigators for a study called Archway recently reported positive Phase III results with the Port Delivery System (PDS) (Roche), an implantable, refillable device that’s designed to continuously release customized ranibizumab formulations into the eye over time. “The need to lessen the treatment burden in patients with nAMD is well established,” the investigators wrote in their paper. “To increase treatment durability, the PDS leverages the well-established efficacy of ranibizumab combined with continuous delivery into the vitreous via the implant for sustained intravitreal VEGF suppression. In Archway, effective nAMD disease control with a reduced treatment frequency was achieved in almost all PDS-treated patients.”
Archway is an open-label, randomized visual acuity assessor-masked noninferiority and equivalence trial. It included patients with nAMD who had been diagnosed within nine months of screening and who had previously received treatment with and were responsive to anti-VEGF therapy.
The researchers randomized 418 patients 3:2 to treatment with PDS with ranibizumab 100mg/mL with fixed 24-week refill-exchanges (PDS Q24w, n=251 with 248 receiving treatment) or intravitreal ranibizumab 0.5mg injections every four weeks (monthly ranibizumab, n=167). The primary study endpoint was change in BCVA from baseline averaged over 36 and 40 weeks.
They reported that baseline BCVA was 74.4 (PDS Q24w) and 75.5 (monthly ranibizumab) ETDRS letters (Snellen equivalent 20/32). Among the PDS Q24W arm, adjusted mean change in BCVA score from baseline averaged over the study period was +0.2 ETDRS letters. In the monthly injection arm, mean change from baseline was +0.5, demonstrating a difference of -0.3). The researchers reported that PDS Q24W was noninferior and equivalent to monthly ranibizumab.
A total of 246 patients treated with PDS were assessed for supplemental ranibizumab treatment. Of the 246 patients, 242 (98.4%) didn’t received supplemental ranibizumab treatment before the first refill-exchange procedure. This included four patients who discontinued treatment before the first refill-exchange.
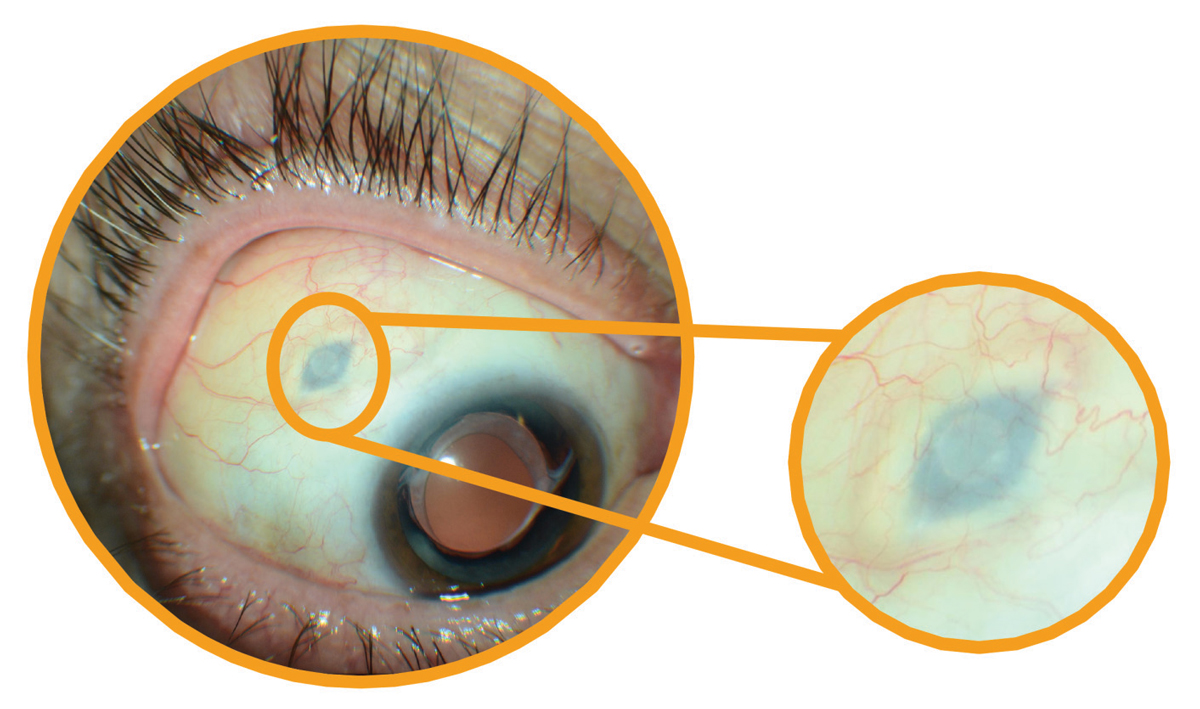
The researchers reported adverse events of special interest in 47 (19%) of PDS patients and in 10 (6%) monthly ranibizumab patients. In PDS patients, adverse events included endophthalmitis (four cases, 1.6%), retinal detachments (two cases, 0.8%), vitreous hemorrhages (13 cases, 5.2%), conjunctival erosions (six cases, 2.4%) and conjunctival retractions (5 cases, 2%). The researchers noted that most of these ocular adverse events in PDS patients occurred within one month of PDS implantation.
All patients in the study had previously undergone anti-VEGF treatment. The researchers said this was to ensure responsiveness. “As such, patients were likely at or approaching the plateau of possible vision gains or reductions in CPT in response to anti-VEGF treatment at the time of enrollment, leaving little opportunity for improvement from baseline in these parameters,” the researchers noted. “Consistent with this, following recovery from the expected transient postsurgery drop in vision in PDS patients, overall vision and anatomical outcomes through week 40 were comparable across treatment arms, with minimal changes from baseline. To note, a post hoc analysis found that patients gained an average of 11 letters before starting the study, after a mean of 4.9 anti-VEGF injections.”
Archway is the first successful Phase III trial of a continuous delivery system for a biologic agent into the vitreous. “By meetings its primary objective, Archway is also the first Phase III trial of a long-acting anti-VEGF treatment that demonstrated noninferior and equivalent visual acuity efficacy to the current standard of care for nAMD, monthly intravitreal anti-VEGF injections,” the investigators noted. “Archway showed that continuous intravitreal delivery of ranibizumab via the PDS resulted in commensurate disease control compared with monthly injections.
“Further, patient interest in the PDS for treatment of nAMD and the importance of a reduced treatment burden was demonstrated by the fact that over 90% of PDS patients preferred PDS treatment over previously received intravitreal injections, even with monthly visits for monitoring.”
Holekamp NM, Campochiaro PA, Chang M, et al. Archway randomized Phase 3 trial of the Port Delivery System with ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. September 28, 2021. [Epub ahead of print]. |

