The more information eye care practitioners have about glaucoma, the more effectively they can diagnose, monitor and treat this disease. Researchers at this years Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) meeting presented some of the latest findings about the relationship between blood pressure and glaucoma, central corneal thickness, the newest and most reliable instruments, and prevention and treatment options.
Blood Pressure
Were less likely to think about blood pressure when diagnosing and monitoring glaucoma than we are about measuring IOP, administering visual field tests and examining the optic nerve. However, new research shows that blood pressure may also play a role in glaucoma.
Researchers in San Francisco and Mumbai, India, found that systemic hypertension in normal-tension glaucoma suspects is significantly associated with an increased rate of progression of optic nerve damage.3403 This retrospective cohort study included 200 eyes (103 patients) suspected of having normal-tension open-angle glaucoma. The patients had large cup-to-disc ratios (>0.5), normal IOP (<22mm Hg) and no peripheral visual field defects. Using regression models, they assessed the effect of hypertension (i.e., at least three consecutive blood pressure measurements >140/90mm Hg) on optic nerve head parameter slopes with the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph (HRT).
Those patients with systemic hypertension showed significant increases in the cup area, cup-to-disc ratio and cup volume over time. The authors state that prospective studies are warranted to confirm this association.
In another study, researchers in Seoul, Korea, evaluated 76 eyes of 76 patients at the University of Ulsan clinic in a one-year period.4780 They analyzed each patients age, spherical equivalent, central corneal thickness (CCT), mean office IOP, mean in-hospital IOP, peak in-hospital IOP, 24-hour IOP fluctuation, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure fluctuation. The researchers found that systemic blood pressure fluctuation was the most consistent clinical risk factor in determining the severity of normal-tension glaucoma.
Given these results, if you detect fluctuating blood pressure in a glaucoma suspect or if a patient reports it, strongly consider initiating glaucoma therapy.
Central Corneal Thickness
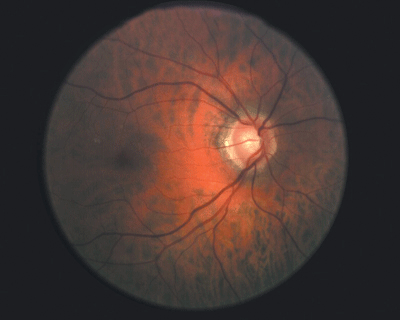
The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS) established the importance of CCT in IOP measurements and as a glaucoma risk factor. The study found that CCT can affect IOP measurements, so adjustments to IOP may be necessary. OHTS also found that CCT is a strong predictor for progression from ocular hypertension to glaucoma.
 |
|
Researchers found that CCT-adjusted IOP may provide a better assessment of the relationship between IOP and open-angle glaucoma prevalence. |
Instruments
Many instruments can help eye care practitioners diagnose glaucoma and follow its progression, so selecting the best ones for your practice can be a difficult decision. The studies below discuss a new glaucoma instrument and confirm the accuracy of those currently available.
Researchers at Columbia University found that the multifocal visual evoked potential (mfVEP), a new objective electrophysiologic test, can detect visual field defects that are not detected by achromatic automated perimetry in glaucoma suspects.4007 The mfVEP also detects progression of the visual field defects.
The mfVEP uses electrodes to record signals that arrive at the visual cortex. Patients view a display that typically contains 60 sectors, each with a checkerboard pattern, arranged in a dartboard array. Each checkerboard has 16 squares (eight black and eight white). The mfVEP measures how the retina and visual cortex respond to light stimuli.
Currently, this new technology is primarily available in teaching institutions and research facilities. It is not yet cost-effective for most eye care practitioners. However, it will likely soon be available to private-practice O.D.s.
Other research at this years ARVO meeting compared glaucoma instruments that are currently available. These include:
 |
| Goldmann applanation tonometry has long been the gold standard for measuring IOP, but researchers found that dynamic contour tonometry may be another useful method for measuring IOP. |
Goldmann applanation tonometry and Perkins hand-held applanation tonometry. Researchers from Loma Linda University in California compared the Goldmann tonometer to the Perkins hand-held applanation tonometer and found that the Perkins tonometer may also be an acceptable method for measuring IOP.4431 They also found that IOP measurements with the Goldmann tonometer were lower (0.29mm Hg) than IOP measurements with the Perkins tonometer.
Prevention
Studies have demonstrated how good nutrition may help prevent or halt the progression of such diseases as age-related macular degeneration and cataract. Research presented at this years ARVO meeting shows that nutrition can also decrease a patients risk for developing glaucoma.
A study that explored the relationship between consumption of fruits and vegetables and glaucoma in 1,274 older ambulatory women found that:3449
Both black and white women who reported eating more than two carrots per week were less likely to have glaucoma than those who reported eating less than one carrot per week.
Consumption of one or more green collards/kale per month was found to be protective against glaucoma, especially among black women, compared to eating less than one per month.
Consumption of more fresh oranges, peaches and spinach was found to be protective against glaucoma in black women.
Treatment
Researchers at Columbia University evaluated the effectiveness of selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT) as a secondary treatment for decreasing IOP and reducing the number of medications taken by patients with glaucoma.5463 They found that SLT significantly lowered mean IOP by 30% and reduced the mean number of required medications by 63% among patients who were medically managed before undergoing SLT. Also, 77% of patients needed one or no medications after they underwent SLT.
SLT is a viable option for glaucoma patients, especially those who cannot afford their medications or in whom the target IOP range cannot be reached. n
Dr. Cole is in private practice in Bridgeton, N.J., and is an assistant professor at Pennsylvania College of Optometry.
2345. Francis BA, Lai M-Y, Azen SP, et al. Relationship of the prevalence of open-angle glaucoma and intraocular pressure and the effects of adjusting for central corneal thickness: the Los Angeles Latino Eye Study (LALES).
3403. Punjabi OS, Bostrom AG, Stamper RL, Lin SC. Effect of hypertension and diabetes on progression of optic nerve damage in normal-tension glaucoma suspects.
3449. Yu F, Coleman AL, Stone KL, et al. Association of fruits and vegetable consumption and glaucoma among older women.
4007. Greenstein VC, Zhang X, Wangsupadilok B, et al. Detecting and monitoring progression of visual field defects in glaucoma suspects with the mfVEP: a longitudinal study.
4431. Hartley JC, Song J. Evaluation of accuracy in Goldmann and Perkins applanation tonometry.
4445. Chalkiadakis IS, Patsea E, Amariotakis G, et al. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry in glaucoma practice.
4780. Choi J, Kim K-H, Kook MS. Systemic blood pressure fluctuation as a consistent risk factor for advanced glaucomatous damage in normal-tension glaucoma.
5463. Gupta A, Jindra LF. Selective laser trabeculoplasty is effective as secondary therapy in decreasing intraocular pressure and in reducing medications in patients with glaucoma.

