 |
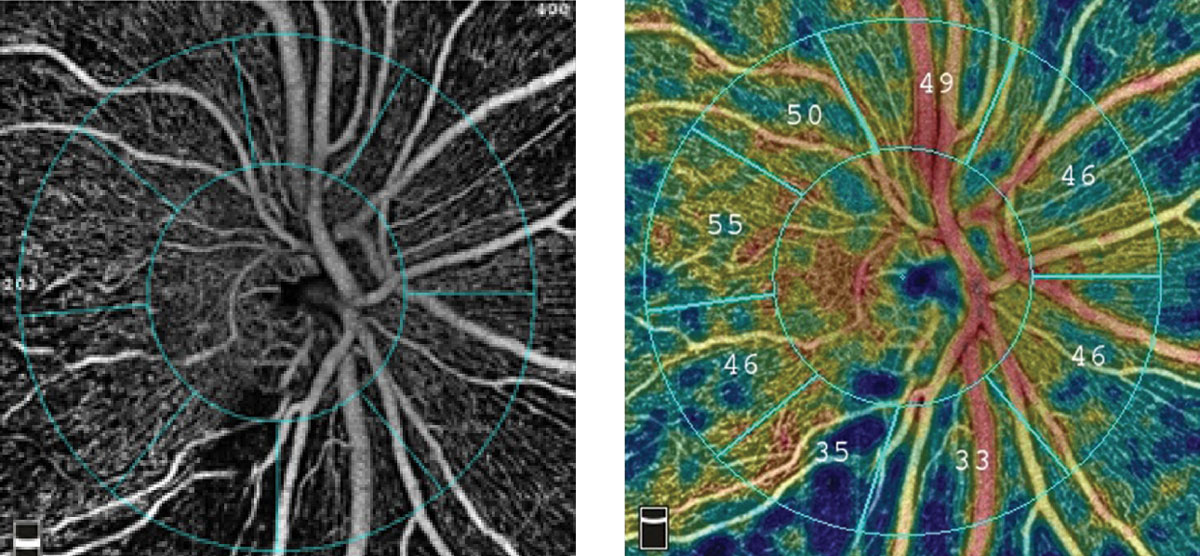
| This study found that measurements of almost all ganglion cell complex thicknesses were associated with worse VA in glaucoma. Photo: Optovue. Click image to enlarge. |
When evaluating glaucoma progression, macular vessel density is a useful parameter, particularly in more advanced disease. Expanding on this, researchers recently sought to determine whether certain OCT and OCT-A parameters correlate with visual acuity (VA) in glaucomatous eyes. The team determined that ganglion cell complex thickness and foveal avascular zone area and circumference are associated with VA in moderate to advanced glaucoma cases but not with early-stage eyes. Superficial and deep vessel density (VD) showed a region-dependent association with VA. The study’s findings were presented earlier this month in Denver at the ARVO 2022 meeting.
The researchers analyzed 144 pseudophakic primary open-angle glaucoma eyes (mean patient age: 80 years old). Foveal VD, parafoveal VD, perifoveal VD and whole-image VD of both superficial and deep layers and their corresponding ganglion cell complex thicknesses were calculated from OCT-A 6mm2 x 6mm2 macular scans. The team also measured the area and circumferences of the foveal avascular zone and the foveal density-300µm.
Multivariable linear mixed model analysis revealed that no OCT/OCT-A parameters correlated with VA in early glaucoma eyes. In the multivariable analysis of moderate to advanced glaucoma, greater foveal avascular zone area and circumference were associated with worse logMAR VA, but foveal density-300µm was not.
Lower measurements of almost all ganglion cell complex thicknesses, including superior hemifield thicknesses, were significantly associated with worse VA, except for the inferior hemifields of the peripheral ganglion cell complex and whole-image ganglion cell complex. For deep VD, only foveal VD was associated with worse logMAR VA. Because the superficial and deep VD showed a region-dependent association with VA, the researchers noted this indicated “the potentially differential involvement of local vasculatures in VA performance.”
Original abstract content © Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology 2022.
Wu J-H, Moghimi S, Nishida T, et al. Association between macular OCT/OCTA parameters and visual acuity in glaucoma. ARVO 2022 annual meeting. |

