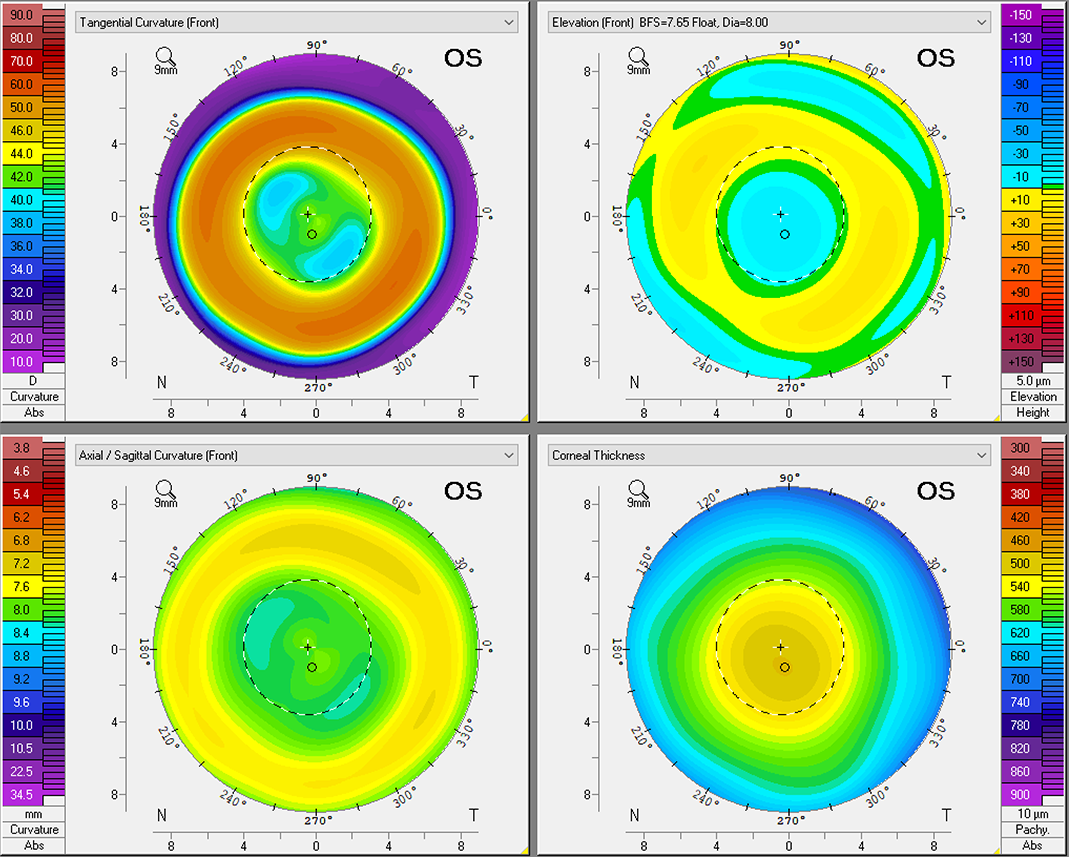
 |
The researchers determined that measuring the distance between the most obvious point within the pigmented arc and the pupil center can also be done with a slit lamp since the pigmented arc is always located in the inferior reverse curve area. Photo: Oculus. Click image to enlarge. |
Studies have found that pigmented arc is a common phenomenon in children treated with orthokeratology (ortho-K) lenses and has been associated with iron deposition in the corneal epithelium, probably due to tears pooling between the irregularly shaped cornea and ortho-k lens. Since the pigmented arc is always located in the inferior reverse curve area, it may indicate lens location on the cornea during lens wear. The anterior segment analyzer Pentacam (Oculus) enables the generation of a three-dimensional model of the anterior segment. A recent study aimed to determine the location and intensity of corneal pigmented arc after lens wear using its densitometry mode. Its team determined that there was a negative correlation between the vertical distance of the pigmented arc and annual axial length (AL) change. They concluded that the Pentacam could provide important information regarding myopia control, next-generation ortho-K design and prescription.
The analysis included 62 eyes from 33 patients (mean age 10.9 years), with a mean follow-up time of 30.6 months. The mean annual AL changes were 0.10 mm.
The researchers found that age statistically correlated with annual AL change. Also, the annual AL change was negatively associated with the relative vertical distance of the lowest density of pigmented arc point based on the visual center, pupil center and corneal thinnest point after adjustment with age.
“In the condition without Pentacam, clinicians can still observe the relative vertical distance from the most obvious point of pigmented arc to the pupil center under a slit lamp to evaluate the efficacy of myopia control,” the study authors wrote. “Since the pigmented arc is always located in the inferior reverse curve area, the ortho-K prescription can be modified to adjust the location of the pigmented arc to benefit myopia control.”
The study indicated that the vertical distance of the lowest density of pigmented arc point to pupil center point and visual center point was influenced by both lens decentration and tilting of ortho-K simultaneously.
“More evidence is needed to clarify the correlation between the amplitude of lens tilting, the amount of decentration and myopia control,” the researchers suggested. “The eyelid may play an essential role in the myopia control efficacy of ortho-K treatment.”
Kuo YK, Chuang LH, Lai CC, et al. Exploring the location of corneal pigmented arc and myopia control efficacy in orthokeratology-treated children using Pentacam measurements. Eye Contact Lens. January 9, 2024. [Epub ahead of print]. |

